About SDPBS
About the Solvers
SDPBS (Solution Decomposition Poisson-Boltzmann Solvers) is a Poisson-Boltzmann equation (PBE) solver library used for the calculation of electrostatics of ionic solvated biomolecules [1]. It is implemented in C++, C, Fortran, and Python. The finite element solver builds upon the state-of-the-art finite element library DOLFIN from the FEniCS project [4].
Finite element meshes are generated by a molecular surface-fitted tetrahedral mesh generator called GAMer-II, which is an extension of a molecular surface and volumetric mesh generation program package reported in [5]. GAMer-II can generate tetrahedral meshes for a rectangular or spherical computational domain and three molecular interfaces - the Gaussian surface, the solvent-excluded surface (SES), and the solvent-accessible surface (SAS) [5,6]. It can adaptively generate the seven overlapped boxes of the computational domain and a mesh of the central box that mixes an uniform Cartesian mesh with an unstructured finite element mesh for our PBE hybrid solver.
SDPBS has two numerical solvers for the nonlinear PBE and the linear PBE - the finite element solver [2], and the finite element-finite difference hybrid solver [3]. It calculates the electrostatics of a protein molecule with np atoms (or other biomolecules or complexes) immersed in a symmetric 1:1 ionic solvent by numerically solving the PBE as follows:
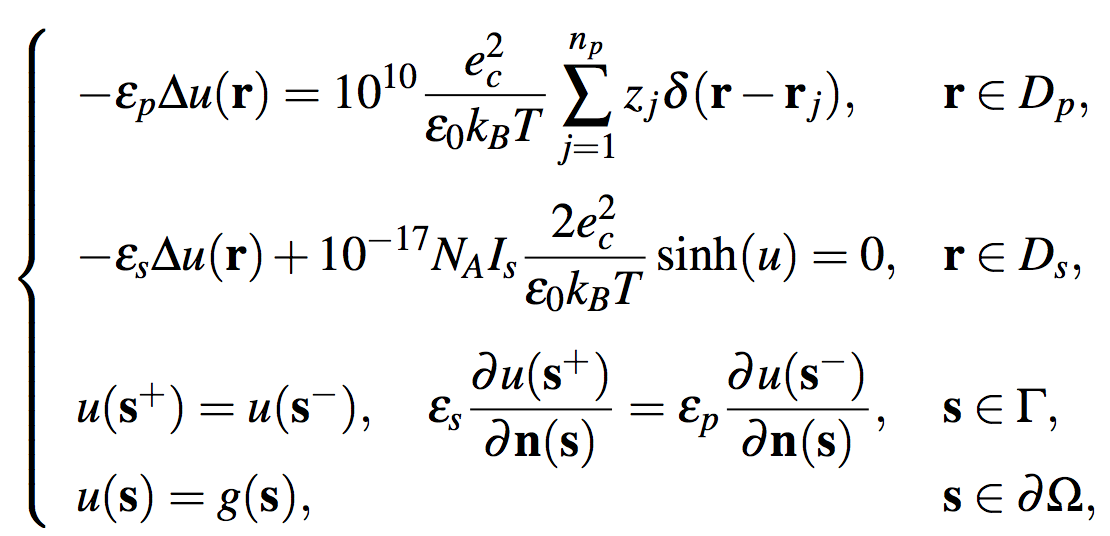
where a computational domain Ω has been partitioned into protein and solvent regions Dp and Ds, as illustrated in Figure 1. The notations used in the equations above are described in Tables 1-3.
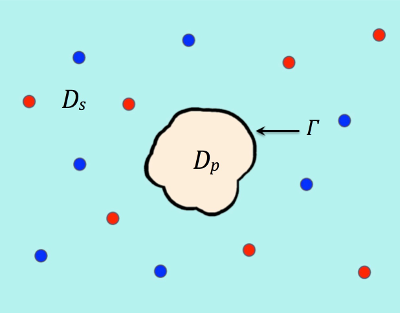
Γ denotes the interface and the two species of ions are colored in red and blue.
Additional Notation
| Parameter | Value | Unit (abbr.) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ε0 | 8.854187817 × 10-12 | Farad/meter (F/m) | Permittivity of vacuum |
| ec | 1.602176565 × 10-19 | Coulomb (C) | Elementary charge |
| kB | 1.380648813 × 10-23 | Joule/Kelvin (J/K) | Boltzmann constant |
| NA | 6.0221409 × 1023 | Mole-1 (mol-1) | Avogadro constant |
| Parameter | Default Value | Unit (abbr.) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| εp | 2.0 | Unitless | Biomolecular region dielectric constant |
| εs | 80.0 | Unitless | Solvent region dielectric constant |
| T | 298.15 | Kelvin (K) | Absolute temperature |
| Is | 0.1 | Mole/Liter (mol/L) | Ionic strength |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Dp | Protein region |
| Ds | Solvent region |
| Γ | Interface between Dp and Ds |
| Ω | Computational domain satisfying Ω = Dp ∪ Ds ∪ Γ |
| ∂Ω | Boundary of Ω |
| rj | Position of atom j (in angstroms) |
| zj | Charge number of atom j |
| n(s) | Unit outward normal vector of Dp |
| g | Boundary value function |
| δ(r − rj) | Dirac-delta distribution at atomic position rj |
References
- Y. Jiang, Y. Xie, J. Ying, D. Xie, and Z. Yu. SDPBS web server for calculation of electrostatics of ionic solvated biomolecules. Molecular Based Mathematical Biology, 3:179-186, 2015.
- D. Xie. New solution decomposition and minimization schemes for Poisson-Boltzmann equation in calculation of biomolecular electrostatics. J. Comput. Phys., 275:294-309, 2014.
- J. Ying and D. Xie. A new finite element and finite difference hybrid method for computing electrostatics of ionic solvated biomolecule. Journal of Computational Physics, 298:636-651, 2015.
- A. Logg, K.-A. Mardal, and G. N. Wells, editors. Automated Solution of Differential Equations by the Finite Element Method, volume 84 of Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering. Springer Verlag, 2012.
- Z. Yu, M.J. Holst, Y. Cheng, and J.A. McCammon. Feature-preserving adaptive mesh generation for molecular shape modeling and simulation. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, 26(8):1370-1380, 2008.
- D. Xu and Y. Zhang. Generating triangulated macromolecular surfaces by Euclidean distance transform. PloS ONE, 4(12):e8140, 2009.
